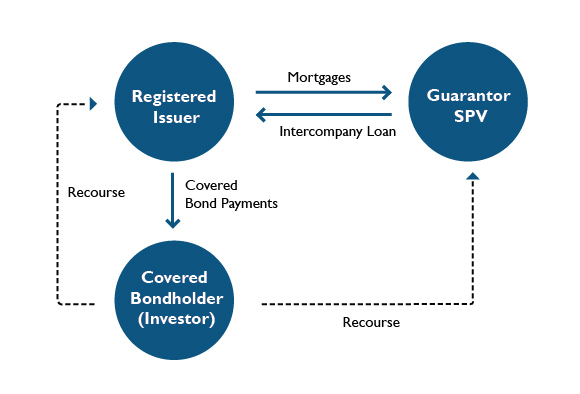
Covered bonds are debt instruments that are issued by a Financial Institution and secured by a pool of assets (the “cover bond collateral”). The issuer of a covered bond pays periodic interest and principal on the bond, in accordance with terms that are set upon issuance.
The covered bond collateral is segregated from the assets of the issuer in the event of insolvency or bankruptcy of the issuer and the pool of covered bond collateral is owned by a bankruptcy-remote special purpose vehicle (SPV) which guarantees the bonds. In the event the issuer defaults on bond payments, the bondholders can look to the SPV and the covered bond collateral for payment.
If the issuer becomes insolvent and the covered bond collateral is insufficient to make the required payments to bondholders, the bondholders (or the bond trustee acting on their behalf) will retain a claim against the issuer for any deficiency in the repayment of all principal, interest and other amounts owing under the bonds.





 Share via Email
Share via Email
